Technical Information Industrial Hoses
General guideline for the use of our industrial hoses
An industrial hose should be selected according to the specific conditions of use to ensure a peak performance of the hose. Therefore, it is essential to obtain as much precise information as possible about the application, the medium to be conveyed and the required connections. Under this section you will find all the important technical information and specifications about our products.
In order to guarantee peak performance of the hose, you should select the type of hose according to specific conditions under which it is to be used. Therefore, it is essential to obtain precise information about the application, the medium that has to be conveyed and the required connections.
The following information is meant to help you in finding the best hose to meet your requirements:
OPERATING CONDITIONS
Medium:
Compounds (e.g. oils, gases and fuels)
Concentrations (chemicals)
Temperature (maximum, minimum)
Pressure:
Pressure load (maximum working pressure)
Suction (maximum low pressure)
Burst pressure, calculated by multiplying the maximum working pressure by the security factor listed in this catalogue
External influences:
Temperature
Atmospheric influences
Contact with oil, fatty substances, seawater or aggressive agents
Bending radius:
The minimum bending radius during usage must not fall below the guidelines specified in this catalogue; otherwise the service-life of the hose will be shortened.
HOSE DIMENSIONS
Inner diameter: Refers to the nominal of the hose
Wall thickness: Refers to the thickness of the hose wall (consisting of tube, reinforcement and cover)
Length: In this column you will find the maximum length of the hose that can be manufactured or the standard supply length, as applicable.
SPECIALS
Norms and Registrations: Under this item you can find on the data sheets the hose norms , or the norms that apply to its rubber mixture, as well as the registrations which Semperit has obtained for its products and its product components.
Identification: Most Semperit hoses have an industrial standard identification. In addition, some hoses can have a three-digit code which is used for internal manufacturing control. Upon request and for larger order quantities, Semperit hoses can also come with a special identification.
The choice of the correct type of hose is very important for the proper and safe use in service.
Therefore when choosing our products, please check the appropriateness of the chosen product for the customer's specific application of you and/or your customer and instruct your customers about the functional range of the products and their limitations accurately.
However the appropriateness of the chosen product for the customer's specific application can only be determined in individual cases and is dependent on the definite installation situation (especially the hose curvature), the combination of the coupling and the compatibility of the medium with the inner coating of the hose (inner core). Further information in the sub-items of this menu (see left side) provide a brief overview on these topics, but do not replace specialist advice in individual cases. Please obtain specialist advice in the event of any uncertainty!
The number of possible operating hours falls if the hose is used under unfavourable operating conditions. These include maximum operational pressure, maximum temperature and minimum bending radius. When several of these factors coincide, the product deteriorates more rapidly and therefore must be replaced sooner.
Therefore please verify the operating conditions regularly and adapt the replacement cycle to them.
Important information
Wrong product selection or improper installation of the hoses can result in damage or failure of the hose, (often also serious) material damage and personal injury. Particularly in applications with high operational pressure, non-compliance with the specifications can result in serious risk of injury! Therefore, in case of doubt, please seek specialist advice!
Hose and working medium
The hose inner surface (inner core) must be appropriate for the medium used in the application (oil, water, air, gas) as otherwise the hose can be damaged or destroyed by working medium or its contents and can thus fail, which can result in (partial or even serious) material damage or personal injury.
Basically every hose consists of the following three elements, each of which fulfills an important function:
1. TUBE
The tube is the inner element of the hose and serves as the contact element for the medium to be conveyed. The choice of the right caoutchouc mixture guarantees the best conveyance of chemicals, oil, abrasive and many other media.
2. REINFORCEMENTS
The reinforcement allows the necessary cross-sectional stability of the hose to resist static and dynamic pressures. This high-strength layer can be made up of diverse textiles, nylon, steel wire or a combination of these materials. If the hose is to be highly flexible or resistant to a high level of suction an additional steel wire helix is embedded in the reinforcement.
3. COVER
The cover is the outer and therefore visible part of the hose. It protects the hose against external influences such as weather, temperature and mechanical damage which may occur during use. It is essential to select the caoutchouc mixture that corresponds best to the conditions for use.
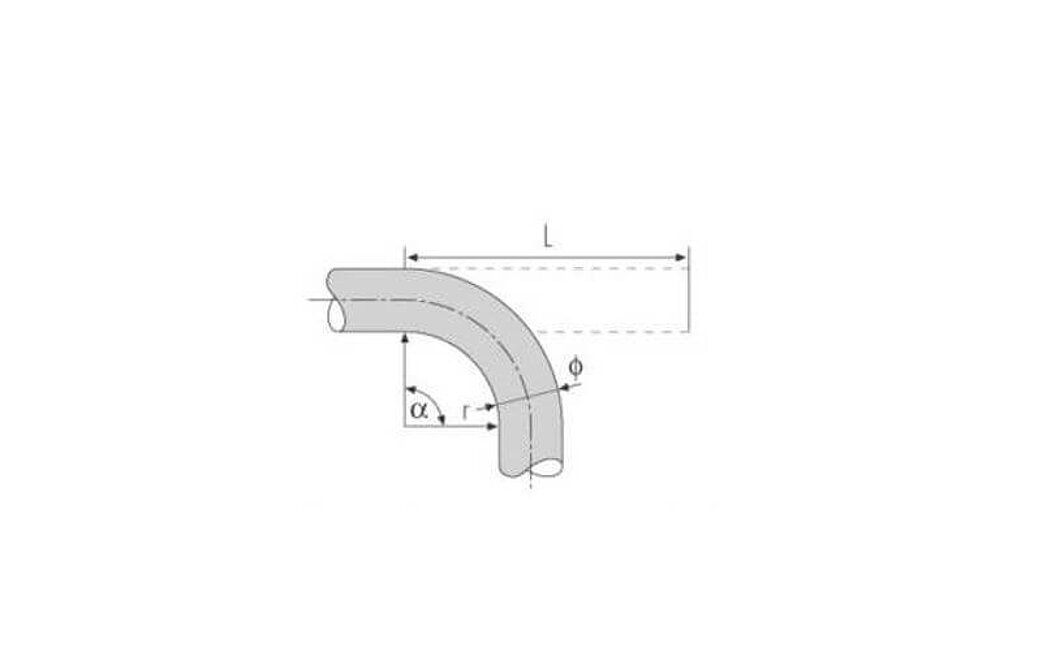
Flexibility and minimum bending radius are important factors in the design and selection of hoses, especially if the hose is to be subject to extreme bending during use.
It must be kept in mind that the expected bending radius in activity is higher than the minimum bending radius of the respective hose. If the radius is less than the minimum bending radius, the hose can kink, contract in the cross-section and even become flat. Thereby the reinforcements can come under excessive strain and may be distorted. This can reduce and even cut short the service life of the hose.
In general the minimum bending radius for every hose is indicated in this catalogue. The hose can be used without difficulties or shortening of its service-life up to the indicated radius. The radius is measured to the inner part of the bend.
The formula used to determine the minimum hose length given the bending radius and the desired degree of bending:
α/360° * 2 π * (r+ϕ /2) =L
Key: a = bending angle, r = given bending radius of the hose,
f = outer radius of the hose,
L = minimum length of the hose.
Example: For bending a hose by 90° which has an external radius of 70 mm, the minimum hose length with a bending radius of 450 mm comes to:
90/360 * 2 π * (450+70 /2) = 762mm
In this case the bend extends over a hose length of a minimum of 762 mm.
SUITABILITY OF THE HOSE
The suitability of the hose is essentially determined by its resistance to the chemical product to be conveyed.
Even during proper use, sufficient resistance does not mean unlimited durability and maintenance of the hose's original properties. The effects from many different kinds of media can include swelling, shrinking and leaking of the hose media, as well as chemical reactions, thereby impairing the properties of the hose and the medium.
In general, this can happen even more quickly and suddenly the higher the working temperature, the greater the working pressure, stream velocity, wear and tear, the longer the duration and the greater the frequency of contact with the substance, the age of the hose, as well as the higher the contamination levels of the chemical substance to be conveyed.
The information contained in this resistance chart is a guideline and can only be guaranteed for a limited period of time.
This is based on laboratory tests generally carried out at a room temperature of 25° C , on relevant literature, as well as on practical experience. Chemical suitability tests are not carried out for every case.
Should the information seem insufficient or should the user be in doubt, s/he should arrange with Semperit Technical Department to have individual testing done.
In addition, the user is also recommended to carry out on-going tests of hose systems if the danger of the above mentioned occurrences cannot be ruled out.
As a rule, the tests should be repeated every six to twelve months.
DEVIATIONS
Should chemical mixtures or chemical substances other than those indicated be conveyed, or should the composition (i.e. the concentration and temperature) of the chemical substances deviate from the given information, you must either consult Semperit before using the hose system in question, or carry out a special chemical suitability test for the relevant application.
The suitability of hoses and hose systems can only be carried out on a case by case basis.
Deviations vis-à-vis Addendum 1 of EN 12115:1999 are possible.
This information is based on years of experience. Right to make technical amendments, literal mistakes and falsities reserved.
SUITABILITY GROUPS
| Suitability group | Suitability | |
| A | suitable | for full and empty hose systems |
| B | limited suitability | i.e. only for empty hose systems or short term operation |
| C | not suitable | Materials will be weakened or destroyed |
| - | contact Semperit |
*) Massenanteil (früher Gewichts-%), TR = technisch rein
**) Siehe Dokumentation Chemieschläuche aus Elastomeren oder Thermoplasten gem. Werknorm Teil 1 der chemischen Industrie, Seite 1
RESISTANCE TO TEMPERATURE
Aging effects with rubber products are always dependent on temperature. A slightly higher temperature causes the hose to age more quickly.
Temperatures above +120° C can reduce the resistance of textile reinforcements as well as the burst pressure of the hose!
Please see the corresponding catalogue sheet for the valid temperature ranges for the respective Semperit hose.
Semperit offers special hoses for high temperature usage.
RESISTANCE TO OIL
The effects of oil and fuel on rubber depend on many factors, which must be observed for the correct selection of materials:
- Oil composition (diesel oil, hydraulic oil, ASTM 1-3)
- Temperature and duration of use
- Pressure / low pressure
Oil resistance of rubber materials is classified according to changes in physical properties that take place in standardized liquids. Swelling in IRM 903 (ASTM oil no. 3) at 100° C for a test duration of 70 hours is often used as a measurement.
If a change in volume of less than 25% is determined, a material is officially classified as having a "very good" resistance to oil.
The usual classifications of rubber hoses with regard to electrical properties are as follows:
- Electrical conductivity, with a resistance of < 106 ohm/meter.
- Antistatic properties, with a resistance of 106 to 109 ohm/meter.
- Insulating properties, with a resistance of > 109 ohm/meter.
The electrical properties of rubber tends to change somewhat with increasing age and wear.
If there are special requirements are needed with regard to the electrical properties of a hose, please specify these when ordering. Our technicians will be happy to help.
Nominal / | Hose production | |||||
| with fixed mandrel | with flexible mandrel | without mandrel | ||||
| min. | max. | min. | max. | min. | max. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,0 - 5,0 | - | - | -0,4 | +0,6 | -0,4 | +0,6 |
| 5,1 - 8,0 | -0,3 | +0,6 | -0,7 | +0,8 | -0,7 | +0,8 |
| 8,1 - 13,0 | -0,3 | +0,6 | -0,8 | +0,8 | -0,8 | +0,8 |
| 13,1 - 16,0 | -0,3 | +0,6 | -0,9 | +0,8 | -0,9 | +0,8 |
| 16,1 - 20,0 | -0,4 | +0,8 | -0,9 | +0,9 | -0,9 | +0,9 |
| 20,1 - 30,0 | -0,4 | +0,8 | -1,2 | +1,2 | -1,2 | +1,2 |
| 30,1 - 40,0 | -0,4 | +1,0 | -1,5 | +1,7 | -1,5 | +1,7 |
| 40,1 - 51,0 | -0,5 | +1,0 | ||||
| 51,1 - 125,0 | -1,0 | +1,0 | ||||
| 125,1 - 160,0 | -1,6 | +1,6 | ||||
| 160,1 - 203,0 | -2,0 | +2,0 | ||||
Length Tolerances
According to EN ISO 1307:2008 the following tolerances apply to Semperit hoses:
| Length | Tolerance |
| to 300 | +/- 3,0 mm |
| > 300 bis 600 | +/- 4,5 mm |
| > 600 bis 900 | +/- 6,0 mm |
| > 900 bis 1200 | +/- 9,0 mm |
| > 1200 bis 1800 | +/- 12,0 mm |
| > 1800 | +/- 1% |
According to EN ISO 1307:2008 the following tolerances apply to Semperit hoses:
Tolerances | ||||||
Nominal / | Hose production | |||||
| with fixed mandrel | with flexible mandrel | without mandrel | ||||
| min. | max. | min. | max. | min. | max. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,2 | 3,2 | 3,8 | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | 4,0 | 4,8 | 4,0 | 4,8 | 3,4 | 4,6 |
| 5 | 4,6 | 5,4 | 4,6 | 5,4 | 4,2 | 5,4 |
| 6,3 | 6,2 | 7,0 | 6,2 | 7,0 | 5,6 | 7,2 |
| 8 | 7,7 | 8,5 | 7,7 | 8,5 | 7,2 | 8,8 |
| 10 | 9,3 | 10,1 | 9,3 | 10,1 | 8,7 | 10,3 |
| 12,5 | 12,3 | 13,5 | 12,3 | 13,5 | 11,9 | 13,5 |
| 16 | 15,5 | 16,7 | 15,5 | 16,7 | 15,1 | 16,7 |
| 19 | 18,6 | 19,8 | 18,6 | 19,8 | 18,3 | 19,9 |
| 20 | 19,6 | 20,8 | 19,6 | 20,8 | 19,3 | 20,9 |
| 25 | 25,0 | 26,4 | 25,0 | 26,4 | 24,2 | 26,6 |
| 31,5 | 31,4 | 33,0 | 31,4 | 33,0 | 30,2 | 33,4 |
| 38 | 37,7 | 39,3 | 37,7 | 39,3 | 36,5 | 39,7 |
| 40 | 39,7 | 41,3 | 39,7 | 41,3 | 38,5 | 41,7 |
| 50 | 49,4 | 51,0 | - | - | 48,1 | 51,6 |
| 51 | 50,4 | 52,0 | - | - | 49,1 | 52,6 |
| 63 | 63,1 | 65,1 | - | - | 61,5 | 65,5 |
| 76 | 74,6 | 77,8 | - | - | 74,2 | 78,2 |
| 80 | 78,6 | 81,8 | - | - | 78,2 | 82,2 |
| 90 | 87,3 | 90,5 | - | - | - | - |
| 100 | 100,0 | 103,2 | - | - | 99,4 | 103,9 |
| 125 | 125,4 | 128,6 | - | - | 124,8 | 129,3 |
| 150 | 150,4 | 154,4 | - | - | 150,2 | 154,7 |
| 160 | - | - | - | - | 162,9 | 167,4 |
| 200 | 200,7 | 205,7 | - | - | 200,2 | 206,2 |
Dimensions which are not specified in EN ISO 1307:2008 are produced according our internal tolerances (in mm) as stated below:
Damaged hoses can not only cause a company unexpected costs, but could also lead to accidents with serious consequences - ramifications that can be prevented by sufficiently adhering to the following points.
Prerequisites for safe hose use:
- Select the appropriate hose in accordance with the working pressure, the conditions under which the hose is to be used and the hose's nominal values
- Use the hose in accordance with relevant norms or other regulations
- Properly secure and transfer the hose correctly and carefully
- Immediately replace damaged hoses
Main causes of damage:
- Mechanical damage
- Exceeding the minimum bending radius
- Excessive tensile strain
- Crushing
- Squeezing
- Conveying unsuitable media
Regular inspections for early detection of damage:
- Perfect condition of outer layer of hose - no tears, blistering, warping, worn or kinked areas
- Proper attachment of the fittings
- Proper transfer of the hose - avoid excessive kinking, excessive tensile strain, forceful twisting
- Checking that hose does not leak
Hoses are subject to a limited service life and the user must be alert to warnings of a pending hose failure, especially when the conditions under which the hose is used require a high working pressure and/or the hose is used to convey dangerous substances.
Safety warning: If the manufacturer's recommendations regarding upkeep, maintenance and storage of the hose in question are not followed, this may lead to the hose's failure to function correctly, which in turn may lead to damage of property or serious bodily injury.
The following contains general instructions as to correct hose storage. Improper storage can significantly shorten hose service life.
Proper handling of hoses
Any kind of misuse in handling hoses for example crushing, breaking, pulling or load with not suitable agents must be avoided.
Avoid dragging the hose over sharp or abrasive surfaces, unless the hose was manufactured especially for this kind of application.
Hoses may only be subjected to their maximum working pressure as indicated. Any change in working pressure should be made gradually so that the hoses are not subject to surges in pressure.
Hoses must not be kinked or driven over, unless otherwise indicated on the data sheets.
When handling large hoses, reels and drums should be used wherever possible. For heavy suction and pressure hoses, used for example in loading and discharging oil, appropriate slings should be used for support.
General inspection
Inspections and hydrostatic tests are to be carried out at regular intervals in order to monitor hose suitability for continued use. A visual inspection of the hose for loose covers, kinks, dents or soft spots must be carried out for the purposes of determining whether reinforcements have either broken or shifted out of position. Couplings or other fittings must be carefully inspected for signs that they are becoming detached from the hose and must be replaced immediately if necessary.
Storage
Storing rubber hoses can be influenced by temperature, air humidity, ozone, daylight, oil solvents, corrosive liquids and vapor, insects, rodents and radioactive materials.
Proper storage of the hoses depends primarily of their size (diameter and length), the quantity to be stored and the packaging materials used. Hoses must not be stacked or piled up in such a way so that the stack weight causes the hoses on the bottom to become damaged. As rubber hoses differ widely in dimension, weight and length, no general recommendations can be given in this sense. A thin-walled hose can withstand less strain than a thick-walled hose or a hose reinforced with a steel wire double helix. Hoses that are delivered coiled must be stored horizontally.
Whenever possible, you should store your hoses in their original package, especially if these containers are wooden crates or cardboard boxes. This kind of packaging also protects the hose from sunlight.
The following contains general instructions for properly storing hoses in accordance with the standards laid down in DIN 7716:1982 "Rubber products; requirements for storage, cleaning and maintenance", Paragraph 3. Improper storage can significantly shorten the service life of the hose.
Storage room: The storage room should be cool, dry, free from dust and moderately well ventilated. Storage out in the open that does not protect against the weather is not suitable.
Temperature: Rubber products should not be stored below -10° C or above +15° C, whereby this limit can be exceeded up to +25° C. Higher temperatures are only allowable for very short periods of time.
Heating: In heated storage rooms rubber products must be protected from heat sources. The distance between the heat source and the stored materials must be at least one meter.
Humidity: Storage in humid storage rooms should be avoided. It is important to make sure that condensation does not form. Best is a relative air humidity not exceeding 65%.
Lighting: Rubber products should be protected from the light, especially from direct sunlight and strong artificial light with a high quantity of UV rays. The windows of the storage rooms are, for this reason, to be covered with a red or orange (but never blue) protective coat of paint. Using normal light bulbs for lighting is preferable.
Ozone: As ozone is particularly harmful, storage rooms must not contain any ozone generating equipment, such as electric motors or other kinds of equipment which could generate a spark or other kind of electrical charge. Combustible gasses and vapours which could generate ozone by way of photochemical processes should be removed.
Finally, all rubber products should be stored according to the "first in, first out" principle, as an unusually long storage period can deteriorate the physical properties of rubber products even under the best of conditions.
There are 3 basic types of marking:
1. Transfer tape
The desired wording or design is printed on a backing film in one or more colours. During vulcanisation, the colour is transferred to the surface of the hose. The film is then removed. This results in a visually appealing and very easily distinguishable marking. You can choose from a variety of colours, colour combinations and font sizes. In principle, the ink transfer marking method is available for all hoses with cloth impression.
2. Coloured marking
Liquid colour is applied either by a transfer wheel or ink-jet printer. White ink is mostly used, but other colours may be used in exceptional circumstances. This type of marking is less expensive than using ink transfer tape, although it is significantly less hard-wearing. This type of marking can be applied to all our hose types.
3. Embossing
The text is embossed into the cover using a wheel or tape. With only a few exceptions, this is only available in the same colour as the cover. Embossing is by far the most durable method, as it is totally compatible with the mix used for the cover. It can be applied to all mandrel built hoses.
DELIVERY QUANTITY
For technical or manufacturing reasons, or because of length specifications or packing units, it may not always be possible to supply exact order quantities. We therefore reserve the right to vary the amount actually supplied and invoiced by +/- 10% or at least 1 coil/piece/reel of the amount ordered.
COIL LENGTH
Mandrel built hoses
standard length: 40m
delivered length: ≥36m
Because of different production needs it might be possible that also lengths ≥36m are delivered. Moreover it could happen for customised orders that up to 10% of the deliveries are sent in short lengths from 10-35,9m at the same price.
Long length hoses
standard length: 40m or 50m
min. 95% of the quantity is delivered in fixed lengths.
max. 5% of the quantity is delivered in short lengths (≥10m).
standard length: 100m
min. 90% of the quantity is delivered in fixed lengths.
max. 10% of the quantity is delivered in short lengths (≥10m).
In general length tolerances according to EN ISO 1307:2006 are executed.
If different delivered lengths are required in individual cases, this has to be clarified at the time of order. Unless otherwise agreed the above rules are applied.
PACKING
Standard packaging for rolled goods made on steel mandrels:
- Packaged as single items, loose in lorry.
The following options are also available on request:
- Stretch-wrapped and/or banded onto pallets
- Unpackaged
- Packed in wooden boxes
- Packed in cardboard half shells
- On drums
Standard packaging for rolled goods made using "long length production":
ID < 25mm: 110cm x 110cm pallet, packed as single items, stretch-wrapped on pallet
ID 25, 28 mm: 80cm x 120cm pallet, packed as single items, stretch-wrapped on pallet
ID > 28mm: 110cm x 110cm pallet, loose, stretch-wrapped on pallet
MINIMUM ORDER QUANTITY FOR MANUFACTURE ITEMS
Depending on product type, size and manufacturing technology, certain minimum order quantities must be observed for manufactured items.
Example of how technology plays a role:
LLH (long-length hose) manufacturing technology ID 25mm: approx. 3000m
MBH (mandrel-built hose) manufacturing technology; ID 25mm; steel mandrel: 600m.
STOCK TYPE
Certain items are stocked by Semperit.
We differentiate between items that are automatically manufactured once stock levels fall below a defined minimum level (LR items), and those for which a batch is not produced when stock is exhausted until a new customer order is placed (L items).
The minimum stock level for LR items is based on sales volumes for the previous period and is adjusted according to average demand. At times of peak demand, there may sometimes be shortages and therefore delivery delays until more hoses are manufactured.
A list of our current stock items can be found either by logging onto our website or obtained from your local sales office.
LR......Preferred stock item with minimum stock level (see description above)
L........Stock item with no minimum stock level
O.......Manufacture item
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE CLEANING OF SEMPERIT FOOD QUALITY HOSES
Semperit food-quality hoses are following requirements specified for the respective product. This ensures that no noxious substances affect the transported food. Please follow the instructions mentioned in the pdf document below to guarantee ideal performance of the hose, to avoid any influence on the smell and taste of the transported goods and to ensure a long life of the hose:
In addition to the general handling guidelines for rubber hoses, it is important to observe the following points when using SIGMA® materials handling hose system due to their large physical dimensions and measurements:
- In principle, SIGMA® hoses are to be handled on pallets regardless of delivery method (coiled, up to DN 152, straight, above that) so as to prevent any damage to the hose.
- When delivered straight, it is recommended that the hoses be handled by two fork lifts.
- A hoisting eye must be used if individual hoses or hose bundles must be moved by forklifts without the use of pallets.
- When transporting the hoses they must be sufficiently secured every time so as to prevent any damage during transport.
- SIGMA® hoses must not be dragged across the ground or over sharp-edged objects despite their size.
- At no time, neither during transport nor storage, may objects be placed on the SIGMA® hose; otherwise embedded wire helixes will be in danger of becoming permanently damaged. Only SIGMA® hoses may be stored on top of each other.
- It is very important to note that pressure sensitivity increases with the increasing nominal bore of the hose.
- Due to the high mass of the SIGMA® materials handling hose system, it is recommended that hoisting equipment and the like be used when handling the hoses for ergonomic reasons.
General overview - for detailed information please see our data sheet.
| Pressure | Temperature | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| kp/cm² | bar | Psi | °C | °F |
0,4 | 0,4 | 5,7 | 108,7 | 227,7 |